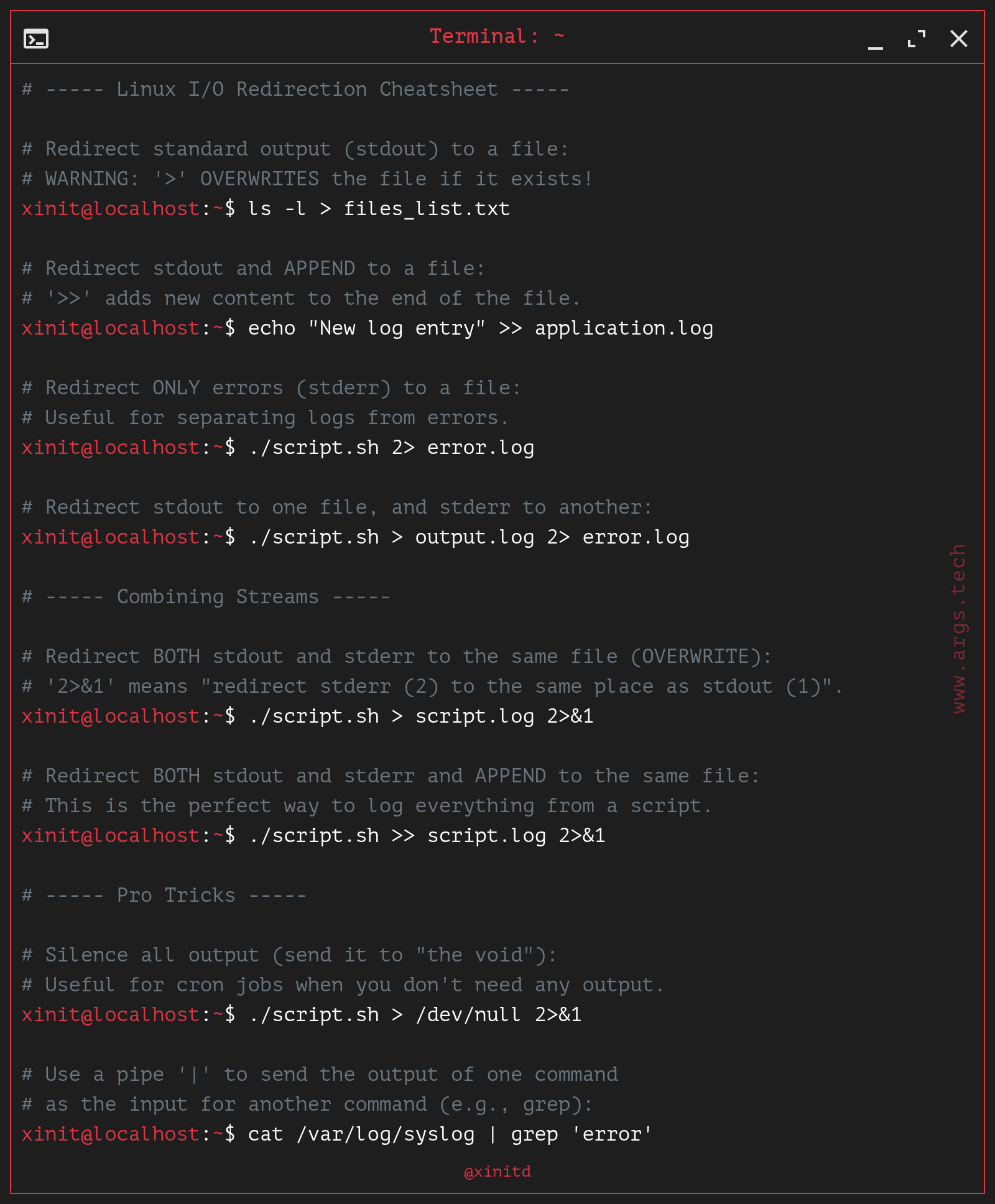
Linux I/O Redirection Cheatsheet (>, >>, 2>&1)
# A simple Linux I/O redirection cheatsheet. Learn how to redirect
# stdin, stdout, and stderr with practical examples of >, <, |, >>, and 2>.
# Master command chaining and error handling in a copy-paste format.
# ----- Linux I/O Redirection Cheatsheet -----
# Redirect standard output (stdout) to a file:
# WARNING: '>' OVERWRITES the file if it exists!
xinit@localhost:~$ ls -l > files_list.txt
# Redirect stdout and APPEND to a file:
# '>>' adds new content to the end of the file.
xinit@localhost:~$ echo "New log entry" >> application.log
# Redirect ONLY errors (stderr) to a file:
# Useful for separating logs from errors.
xinit@localhost:~$ ./script.sh 2> error.log
# Redirect stdout to one file, and stderr to another:
xinit@localhost:~$ ./script.sh > output.log 2> error.log
# ----- Combining Streams -----
# Redirect BOTH stdout and stderr to the same file (OVERWRITE):
# '2>&1' means "redirect stderr (2) to the same place as stdout (1)".
xinit@localhost:~$ ./script.sh > script.log 2>&1
# Redirect BOTH stdout and stderr and APPEND to the same file:
# This is the perfect way to log everything from a script.
xinit@localhost:~$ ./script.sh >> script.log 2>&1
# ----- Pro Tricks -----
# Silence all output (send it to "the void"):
# Useful for cron jobs when you don't need any output.
xinit@localhost:~$ ./script.sh > /dev/null 2>&1
# Use a pipe '|' to send the output of one command
# as the input for another command (e.g., grep):
xinit@localhost:~$ cat /var/log/syslog | grep 'error'