Sending Messages and Files to Users via Telegram Bot API with Python

Introduction
Telegram provides a powerful and simple API for interacting with users via bots. Whether you are building a notification system for your server, a feedback bot, or simply automating daily tasks, the Telegram Bot API is an excellent choice.
You can interact with the API using standard HTTP methods (GET and POST) from any programming language. In this tutorial, we will focus on Python and the requests library to send text messages and files.
Since we will be relying heavily on HTTP requests, having a solid understanding of the requests library is beneficial. I recently published a comprehensive guide on this topic. I highly recommend checking out Python Requests: The Ultimate Guide (GET, POST, File Uploads) to understand the underlying mechanics of what we are about to do.
Prerequisites: Getting started with BotFather
Before writing any code, you need to register your bot and get the credentials.
- Open the Telegram app and search for BotFather.
- Create a new bot by sending the /newbot command and following the instructions.
- Important: Copy the HTTP API Token provided by BotFather. You will need this to authorize your requests.
- Send the /start command to your new bot.
Note: You must manually start the conversation with the bot first. Bots cannot initiate conversations with users who haven't messaged them first to prevent spam.
Sending text messages
To send a text message, we use the sendMessage method. This method requires an HTTP POST request to the following URL structure:
https://api.telegram.org/bot<YOUR_TOKEN>/sendMessage
We need to construct a JSON payload containing the chat_id (the recipient) and the text (the message content). If you want to format your message (e.g., bold or italic text), you can pass the parse_mode parameter.
Here is the complete Python script to send a 'Hello World!' message with Markdown support:
import requests
def send_text_message(token, chat_id, message):
'''
Sends a text message to a specific Telegram chat.
'''
# Construct the URL using the bot token
url = f'https://api.telegram.org/bot{token}/sendMessage'
# Define the payload
data = {
'chat_id': chat_id,
'text': message,
# Optional: Use 'Markdown' or 'HTML' to style your message
'parse_mode': 'Markdown'
}
# Send the POST request
response = requests.post(url=url, data=data)
return response
# Usage example
# Replace 'your_token_here' with the token from BotFather
# Replace 123456789 with your actual user ID (you can find this via @userinfobot)
send_text_message('your_token_here', 123456789, '*Hello World!* This is a bold message.')
After running the script, you should receive a message in your Telegram client:
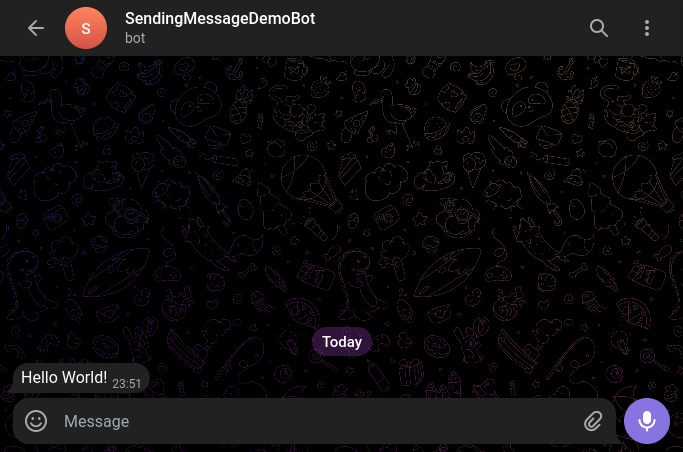
Sending documents and images
Sending files is slightly different. Instead of just sending data, we need to handle file uploads (multipart/form-data). The endpoint for this action is:
https://api.telegram.org/bot<YOUR_TOKEN>/sendDocument
When using the requests library, we open the file in binary mode ('rb') and pass it to the files parameter.
Here is the Python code to upload and send a document:
import requests
def send_document(token, chat_id, file_path):
'''
Sends a document (or image as a file) to a specific Telegram chat.
'''
# Construct the URL for sending documents
url = f'https://api.telegram.org/bot{token}/sendDocument'
data = {'chat_id': chat_id}
# Open the file in binary mode ('rb') so requests can stream it
with open(file_path, 'rb') as document:
files = {'document': document}
# Send the POST request with both 'data' and 'files'
response = requests.post(url=url, data=data, files=files)
return response
# Usage example
# Ensure the file path is correct
send_document('your_token_here', 123456789, '/path/to/your/image_or_doc.png')
If successful, the bot will send the file to the chat, and it will be available for download or preview:
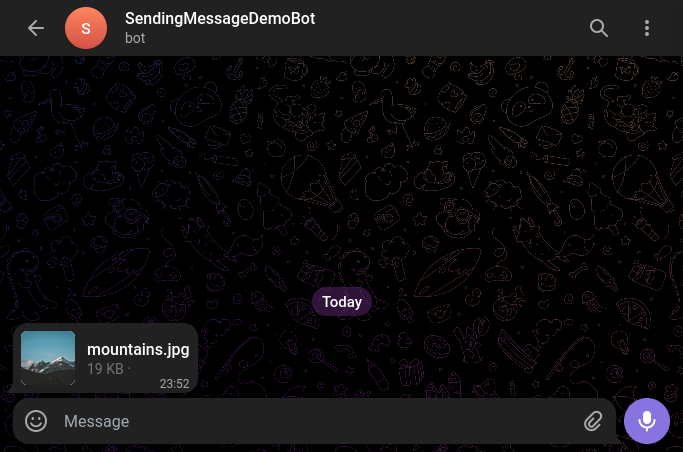
Conclusion
Interacting with the Telegram Bot API using Python is straightforward thanks to the requests library. You can easily expand on this by exploring other methods like sendPhoto, sendAudio, or setting up webhooks for receiving messages.
Remember to keep your API Token secure and never commit it to public repositories!